What is work order management?
Work order management is a systematic approach to tracking, organising, and completing maintenance tasks within an organisation. It involves the planning, scheduling, and recording of maintenance activities, whether they are routine inspections, repairs, or emergency fixes. The goal is to ensure that all maintenance work is conducted efficiently, with minimal disruption to operations, and in compliance with regulatory standards.
Types of work orders
Work orders are essentially detailed instructions or tasks issued to maintenance teams or technicians, outlining what needs to be done, when it needs to be done, and how it should be done. These may arise from scheduled maintenance, unexpected equipment failures, or requests from different departments within an organisation.
Understanding the types of work orders is essential for effective work order management. Generally, work orders can be classified into 4 main categories:
Preventive maintenance work orders
These work orders are scheduled regularly to prevent equipment failures and extend the lifespan of assets. Preventive maintenance tasks include inspections, lubrication, adjustments, and part replacements, performed according to predefined schedules based on time, usage, or condition.
Corrective maintenance work orders
Corrective maintenance work orders are generated in response to equipment malfunctions or breakdowns. These work orders aim to diagnose and repair faults to restore normal operation. This type of work order often arises unexpectedly and requires immediate attention to minimise downtime.
Emergency maintenance work orders
These work orders are prioritised above all others due to critical failures that pose significant safety risks or operational disruptions. Emergency maintenance work orders require swift action and often involve coordination across multiple departments to address the issue as quickly as possible.
Inspection work orders
These work orders are created for routine inspections and audits of equipment and facilities. Inspection work orders ensure that assets are in good working condition and comply with safety and regulatory standards. They may also help identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
What are the 7 phases of work order management?
1. Work identification
This initial phase involves identifying and defining the work that needs to be done. It can stem from various sources, such as equipment inspections, operator observations, or service requests. Proper identification ensures that all necessary tasks are documented and prioritised.
2. Work planning
In the planning phase, the scope of the work is defined, and resources are allocated. This includes determining the necessary materials, tools, and personnel required to complete the work. Detailed planning helps prevent delays and ensures that the team is fully prepared.
3. Work scheduling
Scheduling involves setting a timeline for when the work will be carried out. This phase takes into account factors like equipment availability, production schedules, and technician availability. Effective scheduling minimises downtime and optimises resource utilisation.
4. Work execution
During this phase, the planned and scheduled work is executed. It involves dispatching maintenance teams, coordinating with other departments, and ensuring that all safety protocols are followed. Proper execution is critical for maintaining operational efficiency and safety.
5. Work completion
After the work is completed, it is essential to verify that all tasks have been carried out as planned. This phase includes conducting inspections, testing equipment, and documenting the work done. Any discrepancies or issues are noted for further action.
6. Work review
The review phase involves analysing the completed work to evaluate its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. This can include reviewing work order data, assessing the efficiency of the process, and gathering feedback from technicians and stakeholders.
7. Work closure
The final phase involves closing out the work order, updating maintenance records, and ensuring all relevant data is entered into the system (logging the time taken, materials used, and any follow-up actions required). Proper closure is essential for accurate record-keeping and future planning.
Benefits of work order management
Improved efficiency
Streamlined work order processes reduce the time and effort required to manage maintenance activities. This leads to quicker response times and better resource allocation.
Enhanced asset reliability
Regular and well-documented maintenance activities help extend the lifespan of assets and reduce the likelihood of unexpected failures, which contributes to more reliable operations and better overall equipment performance.
Cost savings
Efficient work order management helps control maintenance costs by optimising resource use, preventing major repairs through proactive maintenance strategies.
Better compliance
Maintaining accurate records and documentation ensures compliance with industry regulations and standards. This is particularly important in industries where safety and regulatory adherence are critical.
Increased visibility and accountability
A centralised system for work order management provides clear visibility into the status of maintenance activities. It also fosters accountability by tracking who is responsible for each task and the outcomes achieved.
Data-driven decision making
Using the right work order management sofware allows you to generate data that can be analysed to identify trends, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. The result? Better decision-making and strategic planning.
Best practices for work order management
Standardise processes
Develop and implement standard operating procedures (SOPs) for creating, assigning, and completing work orders, to ensure consistency and reduces errors. Use a prioritisation system to categorise work orders based on urgency and impact.
Leverage technology
Use an Intelligent Maintenance Management Platform (IMMP) as the ultimate work order management software. An IMMP allows you to centralise data, automate workflows, and provide real-time visibility into maintenance activities.
Ensure accurate documentation
Maintain comprehensive records of all maintenance activities, including the work performed, materials used, and follow-up actions. Accurate documentation supports compliance and future planning, and an IMMP is also ideal for that.
Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Track and analyse KPIs such as work order completion times, first-time fix rates, and planned vs. unplanned work ratios.
Foster communication and collaboration
Encourage open communication and collaboration among maintenance teams, operators, service providers, and management. (See how an IMMP can help here too!).
Continuous improvement
Implement a continuous improvement approach, regularly reviewing and refining work order processes based on data analysis and feedback. This proactive approach ensures that the system evolves to meet changing needs and challenges.
Using Infraspeak for work order management
An Intelligent Maintenance Management Platform (IMMP) like Infraspeak integrates everything you need from a maintenance management solution into a single, cohesive system.
It is a centralised database: all maintenance-related data, including work orders, asset information, inventory, and personnel, can be stored (and used!) there. No more spreadsheets and outdated register systems.
It uses intelligence for work order generation: Thanks to the Infraspeak Gear™, our intelligent core, you’ll receive work order suggestions based on predefined schedules, condition monitoring data, asset history, or service requests.
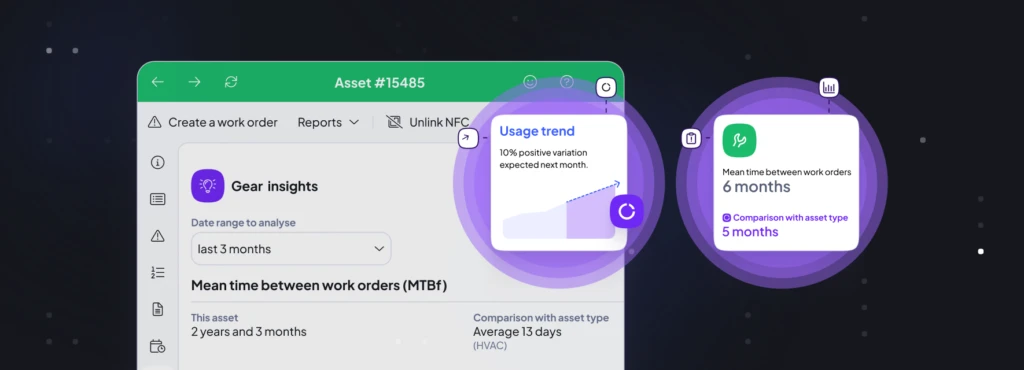
It allows for real-time tracking and monitoring: With an IMMP, organisations can track the status of work orders in real time, monitor technician progress, and receive updates on task completion. Better coordination, better response times. 🤝
It’s 100% mobile accessible: technicians can receive work orders, update status, and access documentation directly from the field.
It gives you the data you really need: IMMPs provide robust analytics and reporting tools so you can easily analyse maintenance performance, identify trends, and optimise processes.
It integrates with other systems: PMS, BIM, ERP, you name it. Infraspeak scales with your business by integrating it with the right tool, at the right time.
And, finally — it’s collaborative. Imagine you needed to hire a contractor to complete a maintenance task. Thanks to the Infraspeak Network™, you can request a quote directly from the work order you’re working on, all from the same app — no need to jump around the platform from one app to another. Get to know more about how to use the Infraspeak Network™ to manage procurement here.


