Preventive maintenance is an important part of the management of any type of infrastructure, contributing to the increase of equipment lifetime, the decrease of unplanned downtime, and, ultimately, the reduction of long-term maintenance costs.
In this ultimate guide, we explore what preventive maintenance is and what it consists of, why it is so important, what its advantages and disadvantages are, how to create a preventive maintenance plan, and how to outline a schedule. We also provide examples and a preventive maintenance plan template in Excel, for free download.
What is preventive maintenance?
Preventive maintenance consists of interventions that prevent breakdowns and decrease the probability of an asset failing. That is, it is a type of planned maintenance that is performed even when a piece of equipment maintains its operational capacity.
It can be as simple as cleaning the filters on HVAC appliances or inspecting the bearings on centrifugal pumps, but it also includes more complex inspection plans, calibration and/or gauging plans, detection of gas leaks and other cyclic revisions.

Types of preventive maintenance
Generally, we can divide it into two main types:
- time-based, i.e. periodic reviews performed at previously defined periods, regardless of asset utilisation (e.g. periodic inspection of elevators every 2 years or elevators every 6 years).
- usage-based, i.e. based on the actual use of the assets, such as the lubrication of a machine every x production cycles (every 500 uses, as an example) or the review of the fleet vehicles when they reach a certain mileage (10,000 km).
Some consider that there are two other types of preventive maintenance – predictive maintenance and prescriptive maintenance. Still, although they share the goal of preventing breakdowns and asset collapse, there are substantial differences between these three types of maintenance:
- predictive maintenance focuses on predicting when a failure will occur to prevent it. Unlike preventive maintenance, which is scheduled and follows predefined time or usage milestones, it is based on the condition of the equipment. Check here for more differences between predictive and preventive maintenance.
- prescriptive maintenance uses Artificial Intelligence to prescribe maintenance actions based on the data and indicators collected about each equipment. Therefore, it requires a high level of computerisation and is associated with Industry 4.0.
Applications of preventive maintenance
In what situations is it advisable to use a preventive maintenance strategy? In which cases is it best to maintain a purely reactive approach? Taking into account the types mentioned above, let see in which situations this strategy is recommended.
❌ When NOT to use preventive maintenance
Let’s start by discarding those assets where we cannot use this technique. If this type of maintenance is based on scheduling, equipment that fails randomly is automatically excluded – such as a bulb that goes out, bells, battery controls, or clogged flushes.
Usually, if it is not possible to establish a standard for the breakdowns of an asset, preventive is not the best option.
✅ When preventive maintenance is recommended
On the other side of the coin, we have the assets whose probability of failure increases with time and use. In these cases, there is a pattern – we can schedule maintenance by following statistics about the expected operation of the equipment and the manufacturer’s recommendations.
That being said, planned maintenance allows us (1) to increase the lifetime of the asset under consideration and (2) to maintain productivity over time.
We then come to the conclusion that preventive maintenance should be applied to assets that are essential to maintain the normal operation of the company, as well as assets of greater value, whose repair or replacement is more expensive than regular preventive activities.
Excessive preventive maintenance (which is possible, taking into account that it can generate unnecessary maintenance actions) and its application to assets of low value or priority may result in costs too high concerning the downtime it prevents, as shown in the following graph: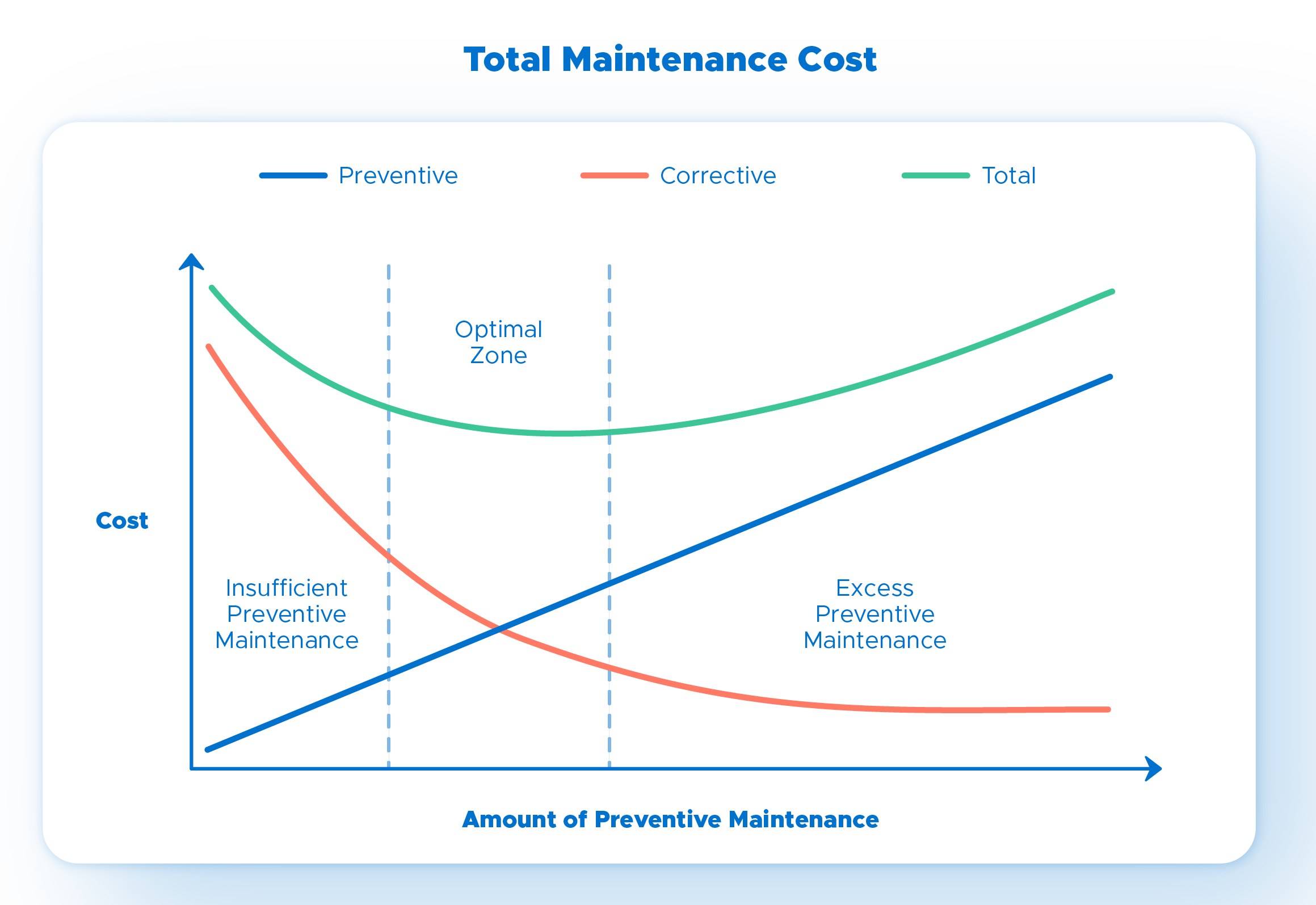
In the case of manufacturing, the priority assets are the machines essential to production. In public buildings, the cleaning of water tanks to prevent outbreaks of Legionella is a good example of preventive maintenance.
Why is preventive maintenance so important?
As seen already, preventive maintenance increases the lifetime of assets and the percentage of planned maintenance. But that is not the only justification to invest in preventive maintenance. Ultimately, preventive maintenance is also a great contributor to keeping your customers satisfied.
-
Reducing downtime and increasing effectiveness (OEE)
It avoids unscheduled downtime, which increases equipment uptime and availability, improving the overall efficiency of the equipment (learn more about OEE). As a consequence, you get a higher return on your equipment investment and meet the established deadlines with your customers.
-
Increase in asset reliability
Preventive maintenance makes the equipment more reliable: they work properly for longer and have a greater lifetime. Reliability makes it possible to forecast more realistically the operation of the company, production capacity, and revenues.
Any company, both in the secondary and tertiary sectors, needs to guarantee the operationality of its facilities. A hotel, for example, can only accept reservations several months in advance if it can predict how many rooms will actually be available.
-
Reduction of reactive maintenance costs
It reduces the cost of parts and transport – just imagine the cost of ordering a part for the HVAC system overnight from an international supplier. It’s a known fact: emergency maintenance almost always involves very expensive repairs. In the worst-case scenario, a lack of maintenance requires the replacement of the asset.
-
Increased security
Regular overhauls detect wear on parts and keep equipment in optimal condition. This offers more safety to those in contact with the asset, both employees and customers. A clear example is a preventive maintenance on elevators, which prevents someone from getting trapped and offers much more safety to anyone in the building
-
Greater comfort
Whenever we talk about a building used by a large number of people, preventive maintenance also contributes to offering more comfort to its customers. Maintenance ensures that all equipment is in full operation, without having to shut down the entire system to make a repair.
Can you imagine what it would be like to be without air conditioning in the middle of summer to do maintenance? There are things we don’t wish on even our worst enemy.
Creating a preventive maintenance plan (step-by-step)
The benefits of preventive maintenance are undeniable. (Honestly, it would be surprising if at this point you were not yet thinking about applying it to your equipment!) The question is how? Where to start? How to create and execute a preventive maintenance plan? Make yourself comfortable, because we have the answers.
The first step in implementing a preventive maintenance strategy is to define a plan. All work orders must be well defined, taking into consideration materials, parts, the necessary labor, and even the hiring of specialised external services.
👉 The process can be divided into 5 steps:
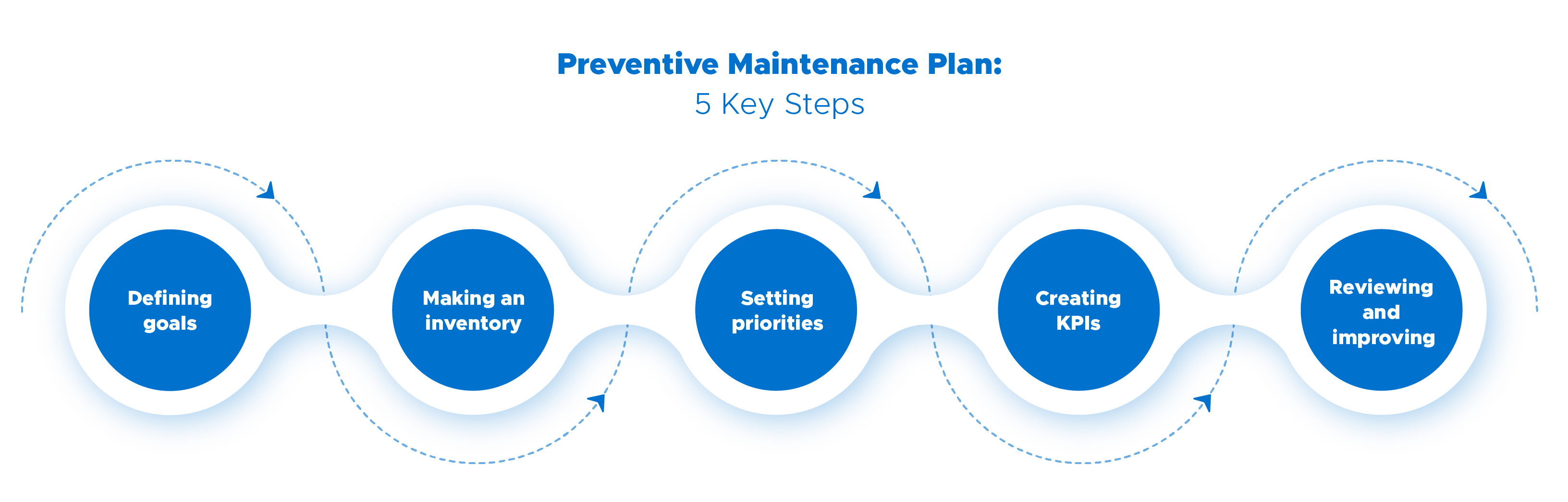
1. Setting goals
To make your plan really useful, the first step is to set the goals you want to achieve. What do you want? To reduce downtime, increase asset reliability, reduce costs, or increase the planned maintenance rate? What have you done so far to meet these goals? What has failed? This first diagnostic test is your starting point
2. Make an asset inventory
For your plan to be comprehensive, you need to map the assets, that is, organise the assets by equipment families and location. Each asset should be linked to the manufacturer’s recommendations, warranties and quality standards to be met.
For example, air conditioning equipment should be grouped into the HVAC equipment family, with the respective location of each appliance and user manuals, as well as the ISO standards (if applicable) to be met.
3. Establish priorities
Both time and resources are limited. Unfortunately, you are unlikely to be able to perform all the preventive maintenance you would like, so give priority to the most critical assets. Select those assets that are essential to the normal operation of the company, those that can cause high losses, and those that pose the greatest risk in the event of failure.
On this later matter, it is important to establish priorities according to the current conditions of the equipment. A risk assessment is extremely useful to rank the priority level of each asset. The inspection of gas leaks, for example, is always a priority because it puts at risk the safety of all those who use the facilities.
4. Creating KPIs for the maintenance plan
To know if the plan is meeting its objectives, the maintenance manager has to be able to track events over time. The best way to do this is through performance indicators (KPIs), which we talk about later on in the assessment and review section of the plan
5. Review and improve the plan
Even the best things can be improved. Depending on the results you get (measured according to the KPIs you defined), make progressive improvements to the plan.
📌 To put this into practice as quickly as possible, we strongly recommend that you read our expert tips on how to create a preventive maintenance plan.
Draw up a preventive maintenance schedule
After creating your plan, you need to define dates, timetables, teams. In short, a preventive maintenance schedule or a work plan.
This work can also be divided into 5 steps
1. Assess labor productivity
For the schedule to be realistic, you need to know how many hours maintenance technicians actually spend performing maintenance work orders (and not looking for tools, on trips, or reading requests). The average is 25-35% of the total hours, but it can go up to 50% with good planning
2. Analyse the maintenance backlog
Evaluate overdue work orders and finish pending work orders before posting to new work orders
3. Adjust the schedule based on the maintenance plan
Determine how many employees, hours, materials, and tools you need for each task in the maintenance plan. You must also define the best days and time to perform scheduled maintenance which forces you to temporarily deactivate assets.
4. Get ready for surprises
Remember that there are always failures that occur randomly. Therefore, your schedule must be flexible enough and must set response times for failures that need reactive maintenance. Any “unforeseen” event that arises during planned actions should always be categorised as reactive maintenance
5. Schedule the work orders
The final step is to schedule the work orders by day and time, with all the information so that the maintenance personnel can perform preventive maintenance safely and effectively.
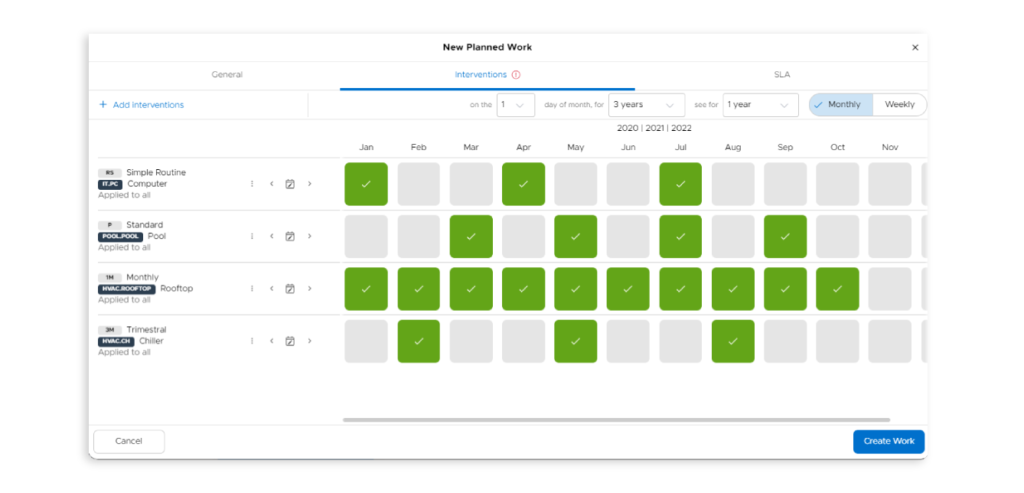
Are you ready to go from theory to practice?
See in detail how to organise your preventive maintenance schedule.
Automation of preventive maintenance work orders
One of the greatest difficulties in drawing up a maintenance plan is mapping assets and cross-checking them with recommended repairs or inspections. In infrastructures with a large number of assets, it is almost humanly impossible to organise the entire inventory.
Fortunately, it is possible to automate most preventive work orders with maintenance management software (CMMS), or, better yet, Intelligent Maintenance Management Platforms (IMMP).
An IMMP allows you not only to catalog your assets but also to associate them with information such as category, brand, equipment model, serial number, location, supplier, the technician in charge, user manuals, and dates of previous interventions.
Schedule preventive maintenance tasks with an IMMP
All the work of creating preventive maintenance plans for different equipment is made easier with the use of maintenance management platforms.
In addition to being able to automatically schedule work orders that only depend on the passage of time, you can set limits for generating interventions based on usage (steps 2 and 3 of the preventive maintenance plan).

Track the plan in real-time
Another advantage of using an IMMP for the management of preventive maintenance work orders is the monitoring of plans in real-time. The software analyses the data calculates the main KPIs automatically and allows you to review and adapt the plans at any time (steps 4 and 5 of how to make a preventive maintenance plan).
Evaluation and Review of Preventive Maintenance Plan
Regardless of the type of assets, you are managing and the specific KPIs you have defined for your company, there are some metrics and “targets” you should always be aware of.
👉 We remember the golden rules of preventive maintenance:
-
Preventive maintenance compliance
It represents the preventive maintenance rate performed within the established time frame, which must be at least 90%. Learn more about how to calculate preventive maintenance compliance.
-
Scheduled maintenance critical percentage
It should be as close to 100% as possible.
-
80/20 ratio for scheduled and non-scheduled maintenance
At least 80% of the hours spent on maintenance must be for preventive work orders. Only 20% (maximum!) of the time should be spent on reactive maintenance work orders, ideally, 85% of the maintenance should be scheduled.
-
The 10% margin rule
Try to complete all work orders ahead of schedule, with a 10% margin. That is if you have a task to complete in 100 days, try to do it only in 90 (10 days ahead of schedule).📌 If your results fall short of expectations, learn more about how to measure the effectiveness of your maintenance plan and what each of these indicators means.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Preventive Maintenance
If you have been aware of the article so far, the advantages of preventive maintenance are clear. However, it is not always the ideal strategy, and may, for example, result in maintenance operations on equipment that is still in optimal condition, simply because a certain period has passed.
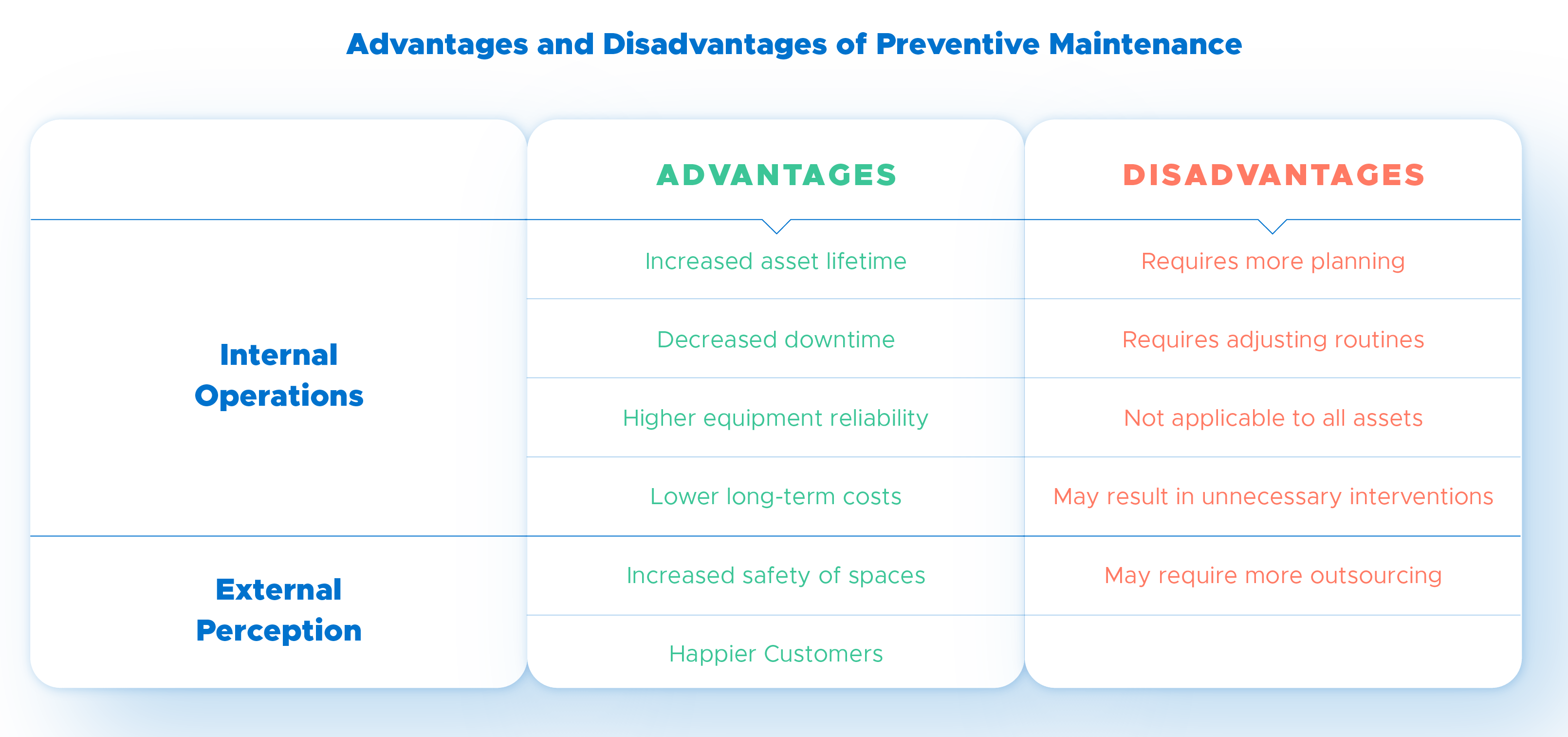
We then review the advantages and disadvantages of preventive maintenance, both in terms of the internal functioning of your operations, as well as the impact on the service provided and the customers’ satisfaction.
What are the advantages?
- Increases equipment lifetime, which increases return on investment;
- Prevents unpredicted stoppages, which improves the operation of the company;
- Improves equipment reliability, which makes forecasts more realistic;
- Reduces maintenance costs on high-value assets: it is less expensive than reactive maintenance and predictive maintenance currently available;
- It is easier to follow a budget for maintenance activities because it predicts (reliably) how you will allocate your resources throughout the year;
- Saves resources, since equipment with operational failures, tend to spend more energy and lose quality;
- More safety on the facilities, since all assets are kept in the best conditions and without wear and tear;
- Meeting deadlines with customers, as there are fewer stoppages and it is easier to predict the output;
- It provides a better customer experience by meeting expectations about the quality of your service – which, in the end, results in loyal customers.
However, preventive maintenance has some disadvantages… What are they?
- It requires more time, both to plan and to inspect;
- You need to readjust your team’s habits and possibly adopt new software;
- It cannot be used on equipment that malfunctions randomly;
- Since it is not condition-based, it can result in unnecessary maintenance activities;
- May result in higher costs if applied to assets of lower value or priority;
- May require more outsourcing maintenance work, forcing you to look for new suppliers;
- To ensure that the deadlines are met, you should negotiate SLAs with suppliers and partners.
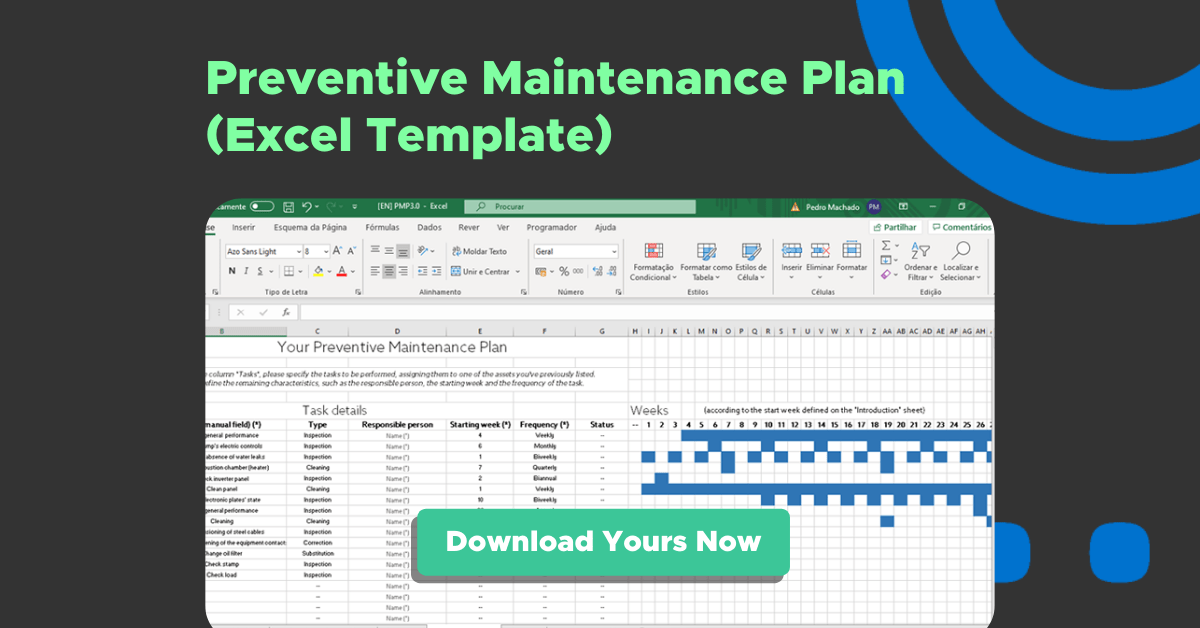
Preventive Maintenance Plan in Excel
You already know what preventive maintenance is and how to adapt it to your business needs. Now, it’s time to get down to business and create a plan.
Download our free template and increase the lifetime of your assets and reduce unplanned downtime.
Schedule, run, and evaluate the performance of your preventive maintenance plans for all your equipment with this fully customizable and easy-to-use Excel document.
📌 Click here to download yours